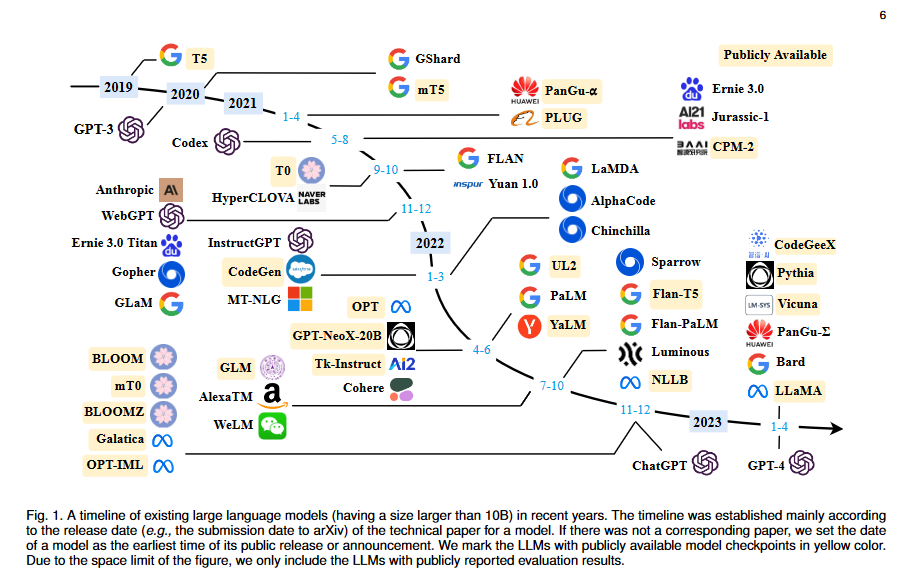
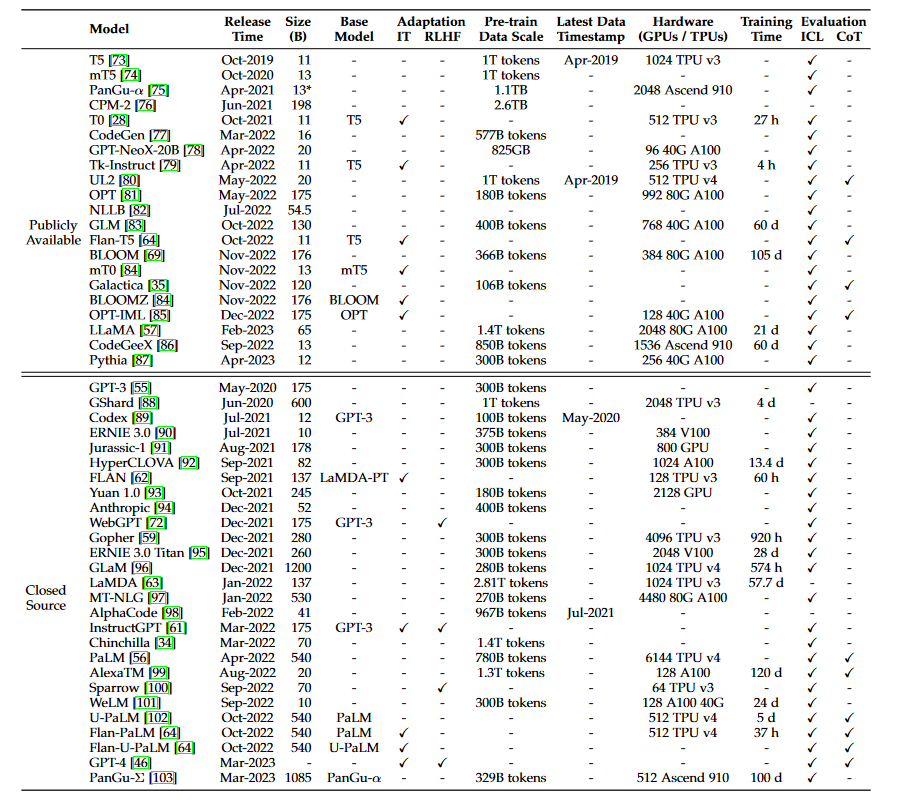
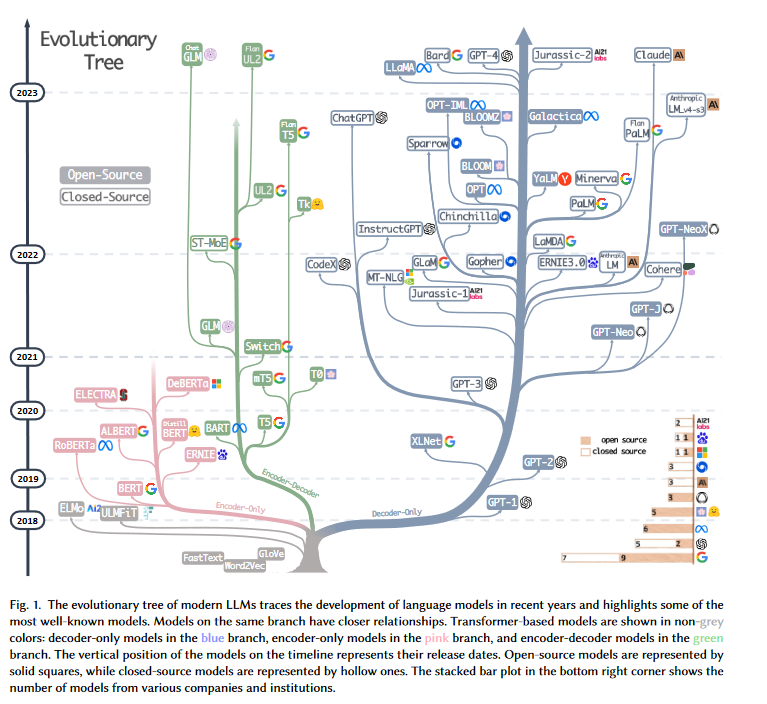
Catching up with the Deep Learning revolution
Timeline
- (dates vary by source)
- two main AI research directions
- symbolic AI
- good match with classic CS
- 1948 - 1966: summer 1
- logic
- logic programming
- theorem provers
- search
- 1966: ELIZA chatbot
- logic
- 1967 - 1977: winter 1
- 1978 - 1987: summer 2
- expert systems
- 1988 - 1993: winter 2
- 1993 - 2012
- Hidden Markov Models (HMM)
- Bayesian reasoning
- decision trees
- 2012 - present
- deep learning (non-symbolic)
- neural networks
- uses techniques typically found in electrical engineering
- 1943 - 1969: wave 1
- 1943: McCulloch-Pitts neuron, neural networks
- neural networks are Turing complete
- 1950: Turing: imitation game (Turing test)
- 1950s: stochastic gradient descent
- 1956: Darthmouth workshop
- 1957: Rosenblatt perceptron
- 1969: Minsky & Papert: Perceptrons book
- pessimism caused decline in neural net funding
- shift towards symbolic AI
- 1943: McCulloch-Pitts neuron, neural networks
- 1969 - 1987: winter
- 1987 - 2012: wave 2
- 1987: Rumelhart: connectionism
- shift from symbolic AI back to neural networks
- hidden layers
- sigmoid activation function
- 1989: Lecun: handwritten digit recognition with CNNs and backpropagation
- 1992: Vapnik: SVM kernel trick
- 1997: LSTM
- 1997: bidirectional RNNs
- 1998: Lecun & Bengio: handwritten character recognition with CNNs
- 2003: Bengio: deep learning for language modeling
- 2006: Hinton: deep learning for handwritten digit recognition
- 1987: Rumelhart: connectionism
- 2012 - present: wave 3 - more compute and storage
- 2012: AlexNet CNN wins ImageNet ILSVRC 2012
- 2014: Goodfellow: GANs
- 2016: Google DeepMind: AlphaGo
- 2017: Google: transformers
- symbolic AI
Information sources
- recent LLM surveys (early 2023)
- books
- ✨ https://www.deeplearningbook.org
- https://aima.cs.berkeley.edu/global-index.html
- http://neuralnetworksanddeeplearning.com
- https://fleuret.org/public/lbdl.pdf
- ✨ https://www.oreilly.com/library/view/designing-machine-learning/9781098107956/
- https://github.com/udlbook/udlbook
- https://github.com/stas00/ml-engineering
- https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch
- newsletters
- tutorials
- blogs
- GAFA
- other
- https://paperswithcode.com
- https://huggingface.co/blog
- https://stability.ai/blog
- https://karpathy.github.io
- https://colah.github.io
- https://jack-clark.net
- https://huyenchip.com/blog
- https://distill.pub
- https://blog.acolyer.org
- https://neptune.ai/blog
- https://www.seldon.io/resources/blog
- https://thegradient.pub
- https://pauliusztin.substack.com/
- https://transformer-circuits.pub/
- courses
- classic ML
- https://www.coursera.org/learn/machine-learning by Andrew Ng, Stanford
- https://www.coursera.org/learn/ai-for-everyone by Andrew Ng for non technical people (2019)
- https://app.ai-cursus.nl by The Netherlands
- https://www.elementsofai.com by Finland (2019)
- https://developers.google.com/machine-learning/crash-course
-
https://cloud.google.com/blog/topics/developers-practitioners/ai-all-humans-course-delight-and-inspire
- internal Google course by Cassie Kozyrkov
- https://aws.amazon.com/training/learning-paths/machine-learning
- https://aws.amazon.com/machine-learning/mlu
- https://www.gptandchill.ai/codingproblems
- https://www.deep-ml.com/
- deep learning
- ✨ https://www.3blue1brown.com/topics/neural-networks
- https://course.fast.ai
- https://www.deeplearning.ai
- ✨ https://karpathy.ai/zero-to-hero.html
- https://github.com/karpathy/LLM101n
- https://huggingface.co/learn/nlp-course
- https://www.cloudskillsboost.google/paths/118
- https://microsoft.github.io/generative-ai-for-beginners
- https://d2l.ai
- https://atcold.github.io/NYU-DLSP20
- https://web.stanford.edu/~jurafsky/slp3
- https://fleuret.org/dlc/
- Stanford CS25 - Transformers United
- Jeff Dean: Exciting trends in ML
- Ilya Sutskever's AI reading list for John Carmack
- https://andrewkchan.dev/posts/diffusion.html
- https://arena-ch1-transformers.streamlit.app/[1.1]_Transformer_from_Scratch
- https://github.com/mlabonne/llm-course
- https://github.com/iusztinpaul/hands-on-llms
- classic ML
- podcasts
-
https://www.deepmind.com/the-podcast
- with Hannah Fry
- https://twimlai.com/podcast/twimlai
- https://lexfridman.com/podcast
-
https://www.therobotbrains.ai
- with Pieter Abbeel
-
https://www.deepmind.com/the-podcast
- conferences
- general
- computer vision
- CVPR
- ICCV
- ECCV
- visualizations / misc
- implementations
Important people
- Geoffrey Hinton (1947): Google Brain, 1/3 godfathers of AI, backpropagation
- Yann LeCun (1960): FB, 1/3 godfathers of AI, CNN
- Yoshua Bengio (1964): Deep Learning book, 1/3 godfathers of AI
- Andrew Ng (1976): Google Brain, Baidu, Coursera, deeplearning.ai,
- Ian Goodfellow (1986): Deep Learning book, Google Brain, OpenAI, Apple, GANs, supervised by Ng + Bengio
- François Chollet: Google, Keras
- Aaron Courville
- Pieter Abbeel, prof EE/robotics/AI @ UC Berkeley
- ESAT at KUL
- PhD at Stanford under Andrew Ng
- podcast: The Robot Brains
- Andrej Karpathy: Stanford, Tesla, OpenAI, Eureka Labs
- Chip Huyen: Stanford, Claypot AI, Voltron Data
- Ilya Sutskever: AlexNet, Google, OpenAI
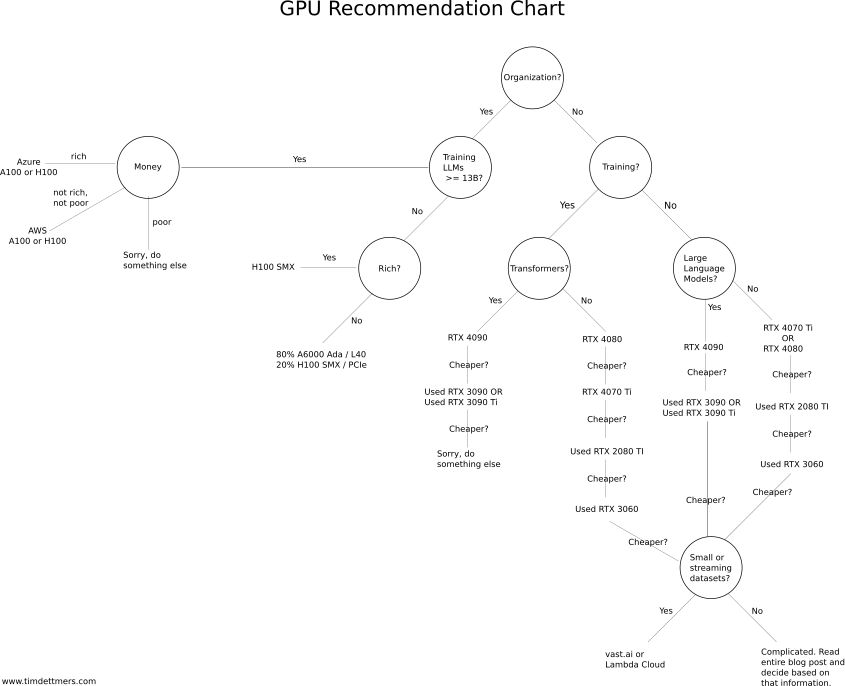
- Tim Dettmers: QLoRA, bitsandbytes, GPU comparison
Modalities
- input
- text
- code
- audio
- speech / voice
- visual
- image
- video
- text
- output
- text
- code
- audio
- speech / voice
- music
- actions
- movement (robots)
- tools/APIs (agents)
- text
Glossary
- AE: auto encoder
- AI: artificial intelligence
- ANN: artificial neural network
- BERT: bidirectional encoder representations from transformers
- BPE: byte pair encoding
- CLIP: contrastive language-image pretraining
- CNN: convolutional neural network
- CoT: chain of thought
- CPU: central processing unit
- DBN: deep belief network
- DL: deep learning
- DNN: deep neural network
- DRL: deep reinforcement learning
- EM: expectation maximization
- Flan: finetuned language model
- FNN: feedforward neural network
- GAN: generative adversarial network
- GPT: generative pre-trained transformer
- GPU: graphical processing unit
- HF: HuggingFace
- LiT: locked image tuning
- LLM: large language model
- LoRA: low-rank adaptation
- LSTM: long short term memory
- ML: machine learning
- MLP: multilayer perceptron
- MoE: mixture of experts
- MP: max pooling
- NLG: natural language generation
- NLP: natural language processing
- NLU: natural language understanding
- PEFT: parameter-efficient fine-tuning
- RAG: retrieval-augmented generation
- RBM: restricted Boltzmann machine
- ReLU: rectified linear unit
- RL: reinforcement learning
- RNN: recurrent neural network
- SFT: supervised finetuning
- SGD: stochastic gradient descent
- SL: supervised learning
- SOTA: state of the art
- SSL: self-supervised learning
- SVM: support vector machines
- TPU: tensor processing unit
- UL: unsupervised learning
- VAE: variational auto encoder
- ViT: vision transformer
- VRAM: video RAM (i.e., the memory of the GPU)
Infrastructure
- you will need one or more Nvidia GPUs
- with CUDA, Tensor Cores and cuDNN support
- overview of recent Nvidia GPU architectures:
| Architecture | Desktop | Workstation | Datacenter |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pascal (2016) | GeForce GTX 10xx | Quadro P | Tesla P4 / Tesla P100 |
| Volta (2017) | N/A | Quadro GV100 | Tesla V100 |
| Turing (2018) | GeForce RTX 20xx | Quadro RTX | Tesla T4 |
| Ampere (2020) | GeForce RTX 30xx | RTX A series | A100 |
| Ada (2022) | GeForce RTX 40xx | RTX 6000 Ada | N/A? |
| Hopper (2022) | N/A | N/A | H100, H200 |
| Blackwell | GeForce RTX 50xx | ? | B100, B200 |
- https://docs.nvidia.com/datacenter/cloud-native/container-toolkit/overview.html
- ✨ https://timdettmers.com/2023/01/30/which-gpu-for-deep-learning
Cloud environments
- https://cloud-gpus.com/
- ✨ https://colab.research.google.com
- tiers
- free tier
- access to Standard GPUs
- e.g., Telse T4 16GB
- access to Standard GPUs
- Colab Pro (~$10/month)
- access to Premium GPUs
- e.g., V100 16GB or A100 40GB (subject to availability)
- access to High RAM environments
- access to Premium GPUs
- free tier
- tiers
| Accelerator | Standard RAM | High RAM* |
|---|---|---|
| None | 12.7 GB | 25.5 GB |
| Standard GPU | 12.7 GB | 25.5 GB |
| Premium GPU* | 12.7 GB | 25.5 GB |
| TPU | 12.7 GB | 35.2 GB |
- https://www.paperspace.com
- https://lambdalabs.com
- https://vast.ai
- https://jarvislabs.ai
- https://modal.com
- https://replicate.com
- https://www.latitude.sh/accelerate
- https://huggingface.co
- https://www.anyscale.com
- https://www.beam.cloud
- traditional cloud
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Microsoft Azure
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
Machine learning libraries
- classic ML
- deep learning
- https://github.com/explosion/spaCy
- https://github.com/facebookresearch/fairscale
- https://github.com/facebookresearch/xformers
- https://github.com/google/jax
-
https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate
- A simple way to launch, train, and use PyTorch models on almost any device and distributed configuration, automatic mixed precision (including fp8), and easy-to-configure FSDP and DeepSpeed support
- https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers
- https://github.com/huggingface/text-generation-inference
- https://github.com/huggingface/transformers
- https://github.com/huggingface/peft
- https://keras.io
- https://pytorch.org
- https://www.tensorflow.org
- tokenizers
- LLM inference runners
- LLM frontends
- embeddings
-
2013-01-16Google word2vec -
2015-09-01Stanford GloVe -
2015-11-09Facebook fastText -
2019-08-27Sentence-BERT -
2022-12-15OpenAI text-embedding-ada-002 - MTEB leaderboard
-
- approximate nearest neighbors (ANN) using vector databases
- Locality Sensitive Hashing (LSH)
- Facebook AI Similarity Search (FAISS; 2017)
- Hierarchical Navigable Small Worlds (HNSW)
-
ScaNN (Google, 2019)
- https://arxiv.org/abs/1908.10396
- each addition requires rebuilding the index
- https://qdrant.tech
- https://www.trychroma.com
- https://www.pinecone.io
- https://weaviate.io
- https://lancedb.com
- https://vespa.ai
- https://github.com/pgvector/pgvector
- https://api.python.langchain.com/en/latest/api_reference.html#module-langchain.vectorstores
- finetuning
-
2019-02-02adapters -
2021-01-01Stanford prefix tuning -
2021-04-18Google soft prompt tuning -
2021-06-17https://github.com/microsoft/LoRA -
2023-05-23https://github.com/artidoro/qlora - https://github.com/huggingface/peft
-
Datasets
- catalogs
- datasets
- text
- CommonCrawl
- Stanford Question Answering Dataset (SQuAD) (2016)
- GLUE (2018)
- OpenWebText (2019)
- Colossal Clean Crawled Corpus (C4) (2019)
- The Pile (2020)
- The Flan Collection (2023)
- MATH (2021)
- wikipedia
- arxiv
- gutenberg
- stackoverflow
- stackexchange
- github
- IMDb
- images
- MNIST (Modified National Institute of Standards and Technology) (1994)
- 28x28 handwritten digits
- train: 60 000
- test: 10 000
-
CIFAR (2009)
- used for training AlexNet
- CIFAR-10
- 10 classes of 6000 32x32 colour images each
- CIFAR-100
- 100 classes of 600 32x32 colour images each
- ImageNet (2009)
- Common Objects in Context (COCO; 2014)
- CelebFaces Attributes (CelebA; 2015)
- Flickr Faces (FFHQ; 2019)
- Met Faces (2020)
-
Large-scale AI Open Network (LAION)
- LAION-400M (2021)
- LAION-5B (2022)
- 5B image-text pairs
- MNIST (Modified National Institute of Standards and Technology) (1994)
- text
Model hubs
- https://huggingface.co/models
- https://www.kaggle.com/models
- tfhub.dev
- https://ai.azure.com/explore/models
Model metrics and benchmarks
Vision models
- outdated
- MNIST error rate
- ImageNet error rate
- recent
- ...
Language models
- note: evaluation often depends not only on eval metric, but also on specific implementation of that metric
- perplexity
- "a measurement of how well a probability model predicts a sample"
- lower is better
- best suited for classic/causal/autoregressive models
- not masked models like BERT
-
Bilingual Evaluation Understudy (BLEU; 2002)
- precision-oriented
- popular for machine translation
- cost-effective
-
Recall-Oriented Understudy for Gisting Evaluation (ROUGE; 2004)
- recall-oriented
- popular for summarization
-
BERTScore (2019)
- cosine similarity based on embedding
- accounts for synonyms, paraphrasing
- cosine similarity based on embedding
- MoverScore (2019)
-
Measuring Massive Multitask Language Understanding (MMLU; 2020)
- test to measure a text model’s multitask accuracy
- covers 57 tasks
- elementary mathematics
- US history
- computer science
- law
- Multilingual Grade School Math (MGSM; 2022)
-
Holistic Evaluation of Language Models (HELM; 2022)
- 7 metrics (accuracy, calibration, robustness, fairness, bias, toxicity, and efficiency)
- 16 core scenarios
-
G-Eval (2023)
- use another LLM as evaluator
- AI2 Reasoning Challenge
- set of grade-school science questions
- HellaSwag
- test of commonsense inference, which is easy for humans (~95%) but challenging for SOTA models
- TruthfulQA
- test to measure a model’s propensity to reproduce falsehoods commonly found online
- EleutherAI Eval
-
AlpacaEval
- for instruction-following LLMs
- HumanEval
- Chatbot Arena